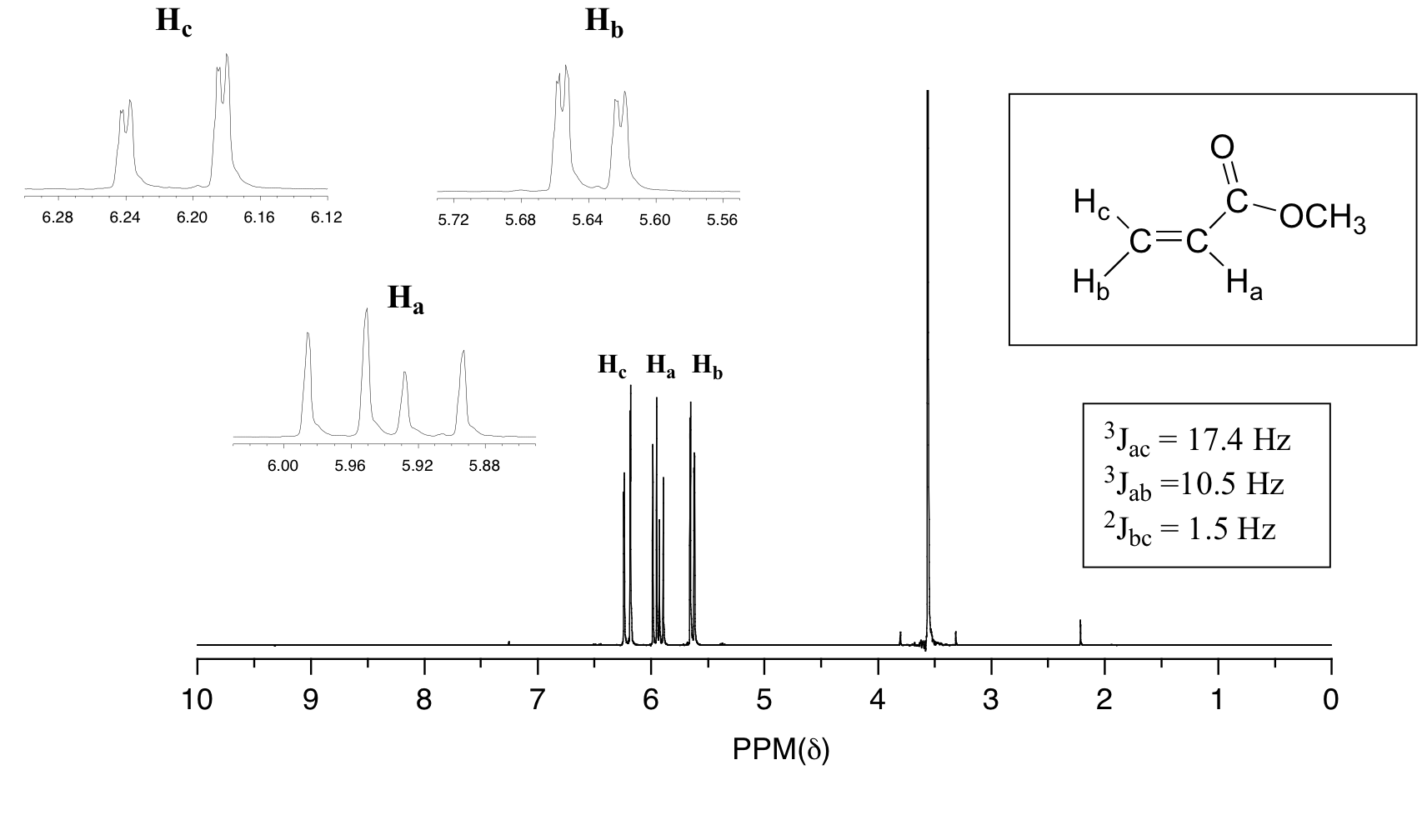
In all of the examples of spin spin coupling that we have seen so far the observed splitting has resulted from the coupling of one set of hydrogens to just one neighboring set of hydrogens.
Where are vinyl hydrogens nmr.
Vinyl aromatics nitriles rocr 3 arcr 2 h alkyne r 3coh o 1h 2nmr shift ranges δ ppm vinyl r 3c f r 3c clrc i r 3c br rccr 3 o δ ppm 13c nmr shift ranges r 2nh r 2ncr h approximate nmr shift ranges note.
0 8 1 5 ppm alkane c h.
Substituents can move the resonance out of the listed range esters amides acids ketones aldehydes.
The key difference between these two structural components is the number of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
These are typical chemical shifts.
This set of pages originates from professor hans reich uw madison structure determination using spectroscopic methods course chem 605.
Tertiary hydrogen vinyl group vinyl chloride vinylic carbocation.
Key difference allyl vs vinyl both allyl and vinyl groups have slightly similar structures with a small variation.
Both groups own a double bond between two carbon atoms where all the other atoms are bonded through single bonds.
When a set of hydrogens is coupled to two or more sets of nonequivalent neighbors the result is a phenomenon called complex coupling a good illustration is provided by the 1 h nmr.
Typical h nmr shift ranges.
It describes nuclear magnetic resonance nmr in details relevant to organic chemistry.
Allyl groups have three carbon atoms and five hydrogen atoms.
The key difference between geminal and vicinal coupling is that geminal coupling refers to the coupling of two hydrogen atoms that are bound to the same carbon atom.
But vicinal coupling refers to the coupling of two hydrogen atoms that are bound to two adjacent carbon atoms.
In samples where natural hydrogen h is used practically all the hydrogen consists of the isotope 1 h hydrogen 1.
It also includes nmr summary data on coupling constants and chemical shift of 1h 13c 19f 31p 77se 11b.
The terms geminal and vicinal coupling come under nmr nuclear magnetic resonance and they describe the differences.
None of the other hydrogens are vinylic.
The vinylic hydrogens are shown in red.
Spectra pdf form of more than 600 compounds are also.
The 2 bond coupling between hydrogens bound to the same alkene carbon referred to as geminal hydrogens is very fine generally 5 hz or lower.
For vinylic hydrogens in a trans configuration we see coupling constants in the range of 3 j 11 18 hz while cis hydrogens couple in the 3 j 6 15 hz range.
1h nmr chemical shifts 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 rh o h r 2ccr h roch 3 ch 3 rch 3 o rh ch 3 ch nh oh rnh 2 o nh 2 rnh 2 roh o oh roh δ ppm type of c hδ ppm description of proton 0 9 alkyl methyl 1 3 alkyl methy lene 1 5 2alkyl methine 1 8 allylic c is next to a pi bond 2 2 3α to carbonyl c is next to c o 2 3 benzylic c is next.