Every expression is either an lvalue or an rvalue so an rvalue is an expression that does not represent an object occupying some identifiable location in memory.
What is rvalue and lvalue in java.
The only mention of them in the language spec is here where it says a variable 4 12 in c this would be called an lvalue.
Lvalue and rvalue in c c programming language.
In java the rvalue and lvalue refer to the expressions on the right and left side of an equality assignment symbol.
So clearly the value 8 in the code above is an rvalue.
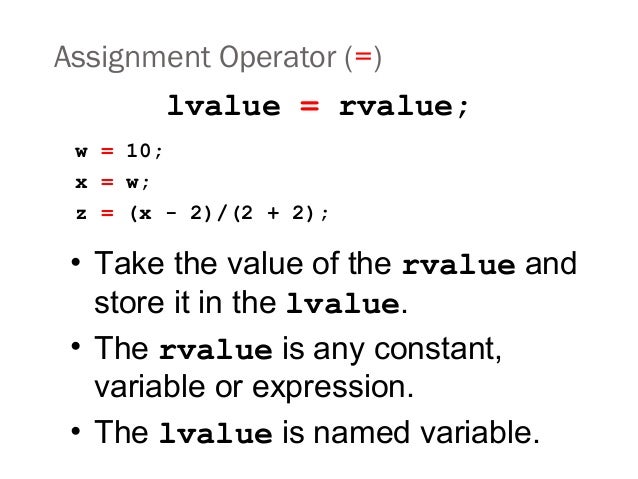
An lvalue is an expression variable constant etc which appears at left hand side of an assignment operator.
Every expression is either an lvalue or an rvalue so an rvalue is an expression that does not represent an object occupying some identifiable location in memory.
Consider the following expression.
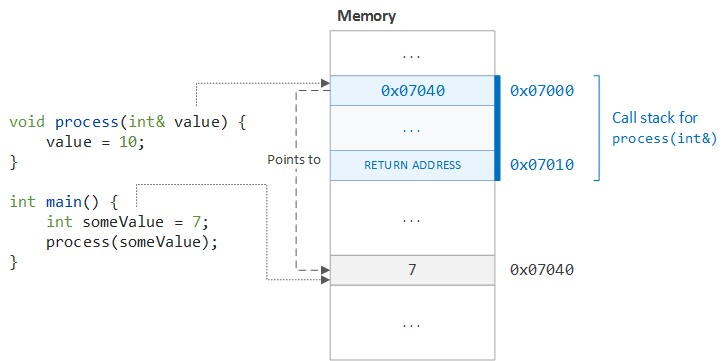
An lvalue locator value represents an object that occupies some identifiable location in memory i e.
In c definition if lvalue and rvalue was somewhat simple anything i e.
But in c this definition has changed and become more interesting.
In this article we will discuss the differences between lvalue and rvalue in c.
Array names and constant identifiers are non modifiable l values and variables objects are modifiable l values.
The rvalue is 5 and lvalue is var1.
Java doesn t really have a concept of lvalues and rvalues.
One could also say that an rvalue is any expression that is not an lvalue.
So if you have.
Learn in an expression what do lvalue and rvalue mean.
Rvalues are defined by exclusion.
An rvalue is basically just an expression which isn t a variable meaning you can t assign a value to it it s the right hand side of an assignment.
An example of an rvalue would be a literal constant something like 8 or 3 14.
Some programming languages use the idea of l values and r values deriving from the typical mode of evaluation on the left and right hand side of an assignment statement an lvalue refers to an object that persists beyond a single expression.
L value may appear as either left hand or right hand side of an assignment operator.
Result is an lvalue.
L value often represents as identifier.
I leave the choice of terminologies to you.
L value refers to memory location which identifies an object.
Lvalue and rvalue in c language last updated.
An lvalue locator value represents an object that occupies some identifiable location in memory i e.
They say that literals constants like 2 a hello 4 5 etc are r values.
An rvalue is an expression variable constant etc which.
An rvalue is any expression that has a value but cannot have a value assigned to it.
In the expression result a b.